Passiflora Colinvauxii: The Story Behind The Discovery And Its Threatened Status
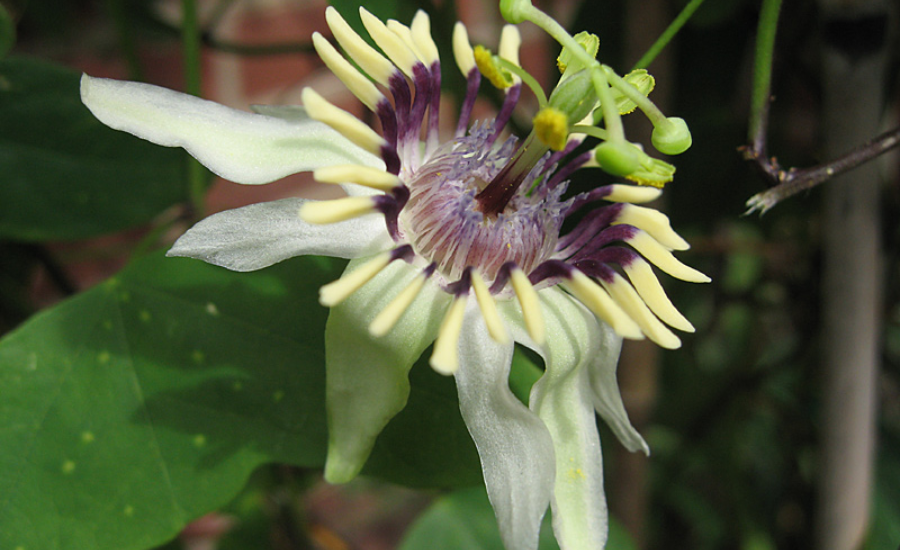
Passiflora colinvauxii, commonly known as a rare species of passionflower, was named in honor of Dr. Paul Colinvaux, a renowned ecologist and author associated with the Marine Biological Laboratory. The plant was first discovered by Dr. Colinvaux in 1966 on the Galápagos Islands, marking a significant moment in botany. This species, recognized for its unique beauty and ecological importance, has captured the interest of botanists and conservationists alike. However, it faces severe threats in its native habitat, highlighting the importance of protecting this rare and valuable plant.
The Discovery Of Passiflora Colinvauxii
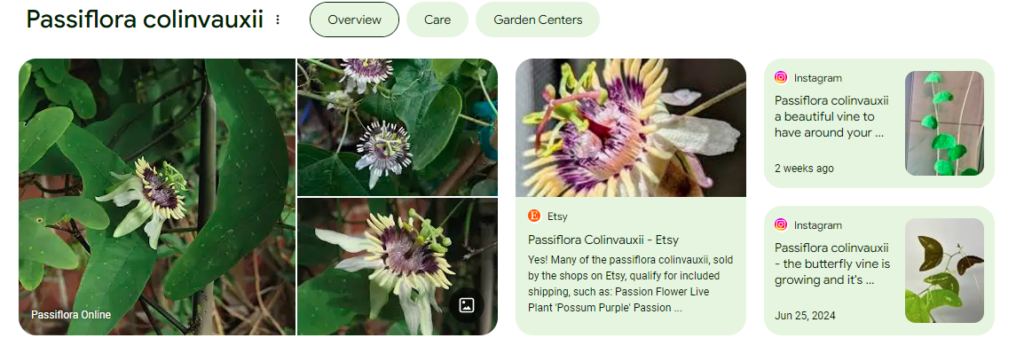
In 1966, Dr. Paul Colinvaux, a renowned ecologist, made a remarkable discovery during his research on the Galápagos Islands. While exploring the unique and diverse ecosystems of these islands, he came across a passionflower species previously unknown to the scientific community. This newly discovered plant, later named Passiflora colinvauxii, became a significant contribution to the field of botany and ecology. Its discovery not only expanded the understanding of plant diversity in the Galápagos but also highlighted the delicate and extraordinary nature of the islands’ flora.
Passiflora colinvauxii is a striking plant with distinctive features that set it apart from other passionflower species. Its ability to thrive in the unique conditions of the Galápagos Islands—such as its volcanic soil, specific climate, and isolated environment—further piqued the interest of researchers. This discovery demonstrated how plants can adapt to specialized ecological niches, providing valuable insights into evolutionary processes and ecological balance. The plant’s adaptation to its environment served as a living example of nature’s ability to innovate and evolve in response to its surroundings.
To honor Dr. Colinvaux’s pioneering work in ecology and his deep commitment to studying the natural world, Passiflora colinvauxii was named in his honor. This tribute reflects not only his academic achievements but also his passion for understanding the intricate relationships between species and their environments. Dr. Colinvaux’s dedication to the Galápagos Islands and his discovery of this unique passionflower species remains an important milestone in the history of ecological research and botany.
The Naming Of Passiflora Colinvauxii
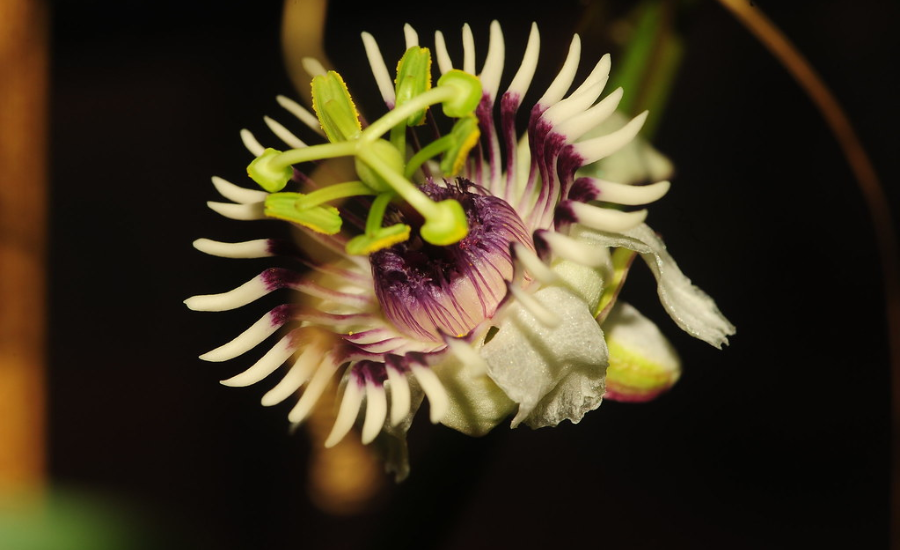

Passiflora colinvauxii was officially named to honor Dr. Paul Colinvaux’s significant contributions to its discovery. His work on the Galápagos Islands in 1966 not only expanded the scientific community’s understanding of the islands’ unique flora but also brought attention to the remarkable passionflower species that had remained previously unknown. As a tribute to his dedication and groundbreaking research, the plant was given the name Passiflora colinvauxii, cementing Dr. Colinvaux’s place in botanical history.
In October 2000, the story of Passiflora colinvauxii took a more personal turn when the author of this article reached out to Dr. Colinvaux. A passionate inquiry about the discovery led to an exchange of letters, facilitated by a simple Google search. Dr. Colinvaux was eager to share the details of his experience, recounting the circumstances of his time on the Galápagos Islands and how he first encountered the mysterious passionflower species. His insights provided an invaluable first-hand account, deepening the understanding of the plant’s significance.
Through this correspondence, Dr. Colinvaux’s personal recollections added a rich, human dimension to the scientific narrative of Passiflora colinvauxii. He described the challenges and excitement he faced while conducting research in such a unique ecosystem. His perspective highlighted not only the plant’s botanical importance but also the profound impact the discovery had on his career and the broader field of ecology. The exchange revealed how deeply Dr. Colinvaux’s observations on the Galápagos Islands in 1966 shaped his view of the natural world and influenced future ecological research.
Passiflora Colinvauxii’s Threatened Status
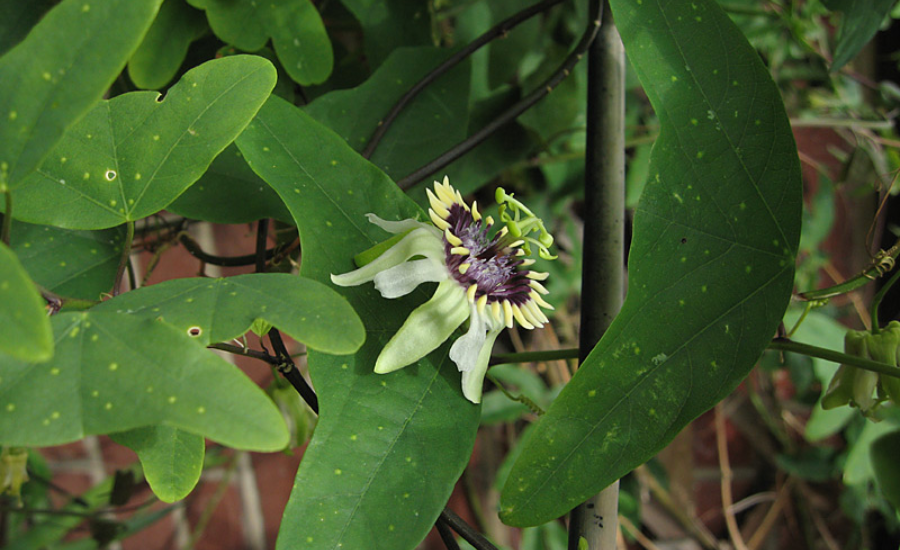

Today, Passiflora colinvauxii faces considerable challenges in its natural habitat, and its future is increasingly uncertain. This unique species of passionflower, once thriving in the distinct ecosystems of the Galápagos Islands, is now listed as one of the 45 species of Passiflora in the 1997 IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants. Its rarity and the threats it faces have earned it the status of being vulnerable to extinction, drawing attention to the pressing need for conservation efforts aimed at preserving its existence.
The decline of Passiflora colinvauxii can be attributed to several environmental factors, most notably habitat destruction. As the Galápagos Islands undergo changes due to human activity, including deforestation and the expansion of infrastructure, the natural habitats of this delicate plant are being altered or lost altogether. In addition to habitat loss, the effects of climate change, such as rising temperatures and unpredictable weather patterns, pose an even greater challenge to the plant’s survival. These environmental changes disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystem, threatening species like Passiflora colinvauxii that depend on specific conditions to thrive.
Invasive species have also contributed significantly to the decline of Passiflora colinvauxii. As non-native plants and animals infiltrate the islands, they compete with the native flora for resources, often outpacing indigenous species in their ability to adapt to the environment. The combined impact of habitat destruction, climate change, and invasive species has resulted in a sharp reduction in the population of Passiflora colinvauxii. Its inclusion on the IUCN Red List emphasizes the urgent need for concerted conservation efforts. Only through sustainable practices, habitat protection, and increased awareness of the dangers facing endangered species can we hope to protect Passiflora colinvauxii and other vulnerable plants from extinction.
The Importance Of Conservation Efforts For Passiflora Colinvauxii
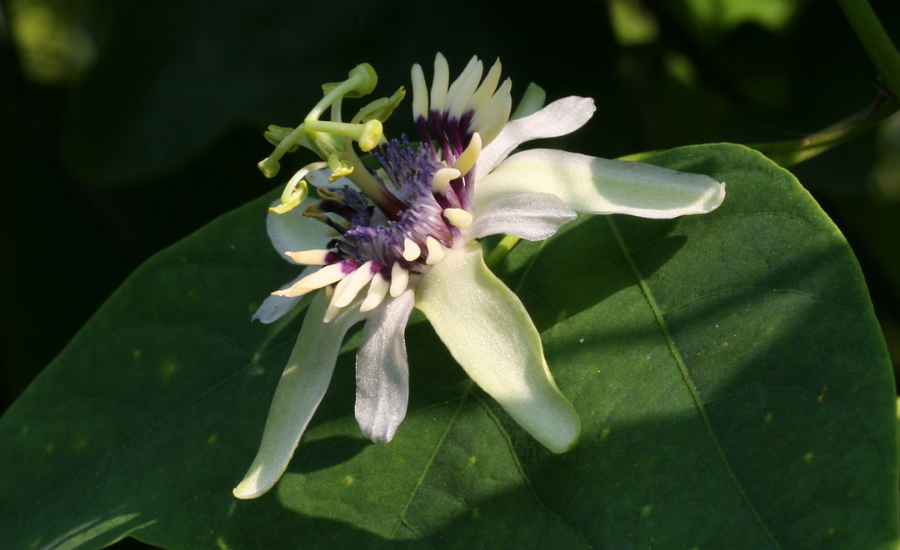

Conserving Passiflora colinvauxii is of paramount importance, not only for the survival of this unique species but also for preserving the intricate balance of the Galápagos Islands’ fragile ecosystem. As one of the many endemic species found on these islands, Passiflora colinvauxii plays a vital role in maintaining the ecological dynamics of the region. Its existence contributes to the complex web of interactions among plants, pollinators, and other organisms, which is essential for the overall health of the environment. The loss of this plant could have ripple effects, potentially disrupting the delicate equilibrium that sustains the islands’ biodiversity.
Efforts to protect Passiflora colinvauxii are not just about safeguarding a single species; they are also about ensuring the survival of numerous other plants and animals that share its habitat. The Galápagos Islands are home to many species that rely on the same ecological niche that Passiflora colinvauxii occupies. By preserving the plant’s natural habitat, conservationists are also protecting the broader ecosystem, offering a refuge for other vulnerable species that could be at risk of extinction. This interconnectedness underscores the importance of holistic conservation strategies that prioritize the entire ecosystem, rather than focusing on individual species alone.
To prevent the extinction of Passiflora colinvauxii, it is essential to raise awareness about its vulnerability and the threats it faces. Conservation programs that educate the public and involve local communities in preservation efforts are critical for the long-term survival of the plant. Increased funding, research, and collaboration with environmental organizations are necessary to create effective protection measures. By prioritizing the conservation of Passiflora colinvauxii, we can help ensure that future generations can continue to appreciate not only this rare plant but also the unique and irreplaceable biodiversity of the Galápagos Islands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Passiflora colinvauxii?
Passiflora colinvauxii is a rare passionflower species found on the Galápagos Islands, discovered by Dr. Paul Colinvaux in 1966. It is known for its unique beauty and ecological significance.
2. Why was it named after Dr. Paul Colinvaux?
The plant was named to honor Dr. Colinvaux’s pioneering research and discovery of this species on the Galápagos Islands.
3. What threats does Passiflora colinvauxii face?
The plant faces threats from habitat loss, climate change, and invasive species, leading to a decline in its population and a vulnerable status on the IUCN Red List.
4. Why is conserving Passiflora colinvauxii important?
Protecting Passiflora colinvauxii helps preserve the Galápagos Islands’ ecosystem, supporting biodiversity and the survival of other species that share its habitat.
5. How can we help protect Passiflora colinvauxii?
Supporting conservation efforts, raising awareness, and advocating for ecosystem protection are key to safeguarding this rare plant and its environment.
Summary
The discovery of Passiflora colinvauxii marked a pivotal moment in botanical and ecological research, shedding light on the remarkable biodiversity of the Galápagos Islands. Named after Dr. Paul Colinvaux, this rare species of passionflower underscores the importance of thorough scientific exploration and the need to protect our natural environments. Today, however, Passiflora colinvauxii faces significant challenges, including habitat loss, climate change, and the spread of invasive species, all of which threaten its survival.
Conservation efforts are crucial to prevent the extinction of this unique plant and preserve the broader ecosystem it supports. Saving Passiflora colinvauxii is not just about protecting a single species, but also about maintaining the fragile ecological balance that sustains countless other organisms in the Galápagos. By honoring Dr. Colinvaux’s legacy, we are reminded of the urgency to adopt sustainable practices and increase global awareness to safeguard the unparalleled biodiversity of this exceptional region.
Get the latest alerts and updates directly: Educake!





